Non-sister Chromatids Are Best Described as Having
A full set of sister chromatids is created during the synthesis phase of. There were also many vague references to the exchange of genetic material rather than DNA or alleles.
Sister Chromatids Online Biology Dictionary
Evidence of crossing over can be seen under the microscope as Xunder the microscope as X--shaped shaped.

. Cohesin is a ring-shaped protein complex. Few candidates successfully described independent assortment as they often failed to. Weve got the study and writing resources you need for your assignments.
The meaning of SISTER CHROMATID is either of the two identical chromatids that are formed by replication of a chromosome during the S phase of the cell cycle are joined by a centromere and segregate into separate daughter cells during anaphase. Sister chromatids are physically held together by cohesin which is a protein complex consisting of four core subunits Fig. Recall that the point of crossing over is to increase genetic diversity.
Hich of the following best describes diffusion passive. Homologous chromosomes pair up and non-sister chromatids exchange genetic material. Sister resolution of single-labelled chromosomes progressively increased from 184 42 in G2 phase up to 460 53 during early mitosis before NEBD progressing to an only slightly higher.
Differentiated sister chromatids coupled with non-random segregation have been proposed to regulate cell fate during the development of multicellular organisms3. Crossing-over occurs during prophase I and it is the exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes. A cell that has two sets of chromosomes is described as being a haploid.
These are called the sex chromosomes. This 14 exchange is called exchange is called crossing ovecrossing over. Segments of DNA that are parts of non-sister chromatids are sometimes exchanged in a process referred to as a gene swapping.
Human females have a homologous pair of X chromosomes XX but males have one X and one Y chromosome XY. Homologous chromatids pair up and non-sister chromosomes exchange genetic material. Some times candidates described chiasmata in relation to sister chromatids rather than non-sister chromatids.
Non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosome pairs exchange segments or parts and Chiasma is formed in these exchanged regions. Chromosomal crossover or crossing over is the exchange of genetic material during sexual reproduction between two homologous chromosomes non-sister chromatids that results in recombinant chromosomes. The synapsis stops with the.
The entire four-stage division process averages about one hour in duration and the period between cell divisions called interphase or interkinesis varies greatly but is considerably longer. Only small parts of the X and Y are homologous. Sister chromatids are BEST described as two DNA molecules that have-different alleles of the same genes arranged in a different order-the same genes in the same order but having different alleles-virtually identical sequences of nucleotides-different genes in the same order and possibly having different alleles of some genes.
The method of pairing the homologous chromosomes is called synapsis. This process is modified during meiosis which produces haploid gametes from a diploid progenitor cell. Up to 24 cash back ____ 47.
The chromosomes remain linked at the sites of crossing over. Over of chromosomes instead of chromatids. Up to 10 cash back By meiosis II only sister chromatids remain and homologous chromosomes have been moved to separate cells.
At pachytene stage crossing over of non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes occurs at the recombination nodules. Mitosis is simply described as having four stagesprophase metaphase anaphase and telophase. In other words a sister chromatid may also be said to be one-half of the duplicated chromosome.
A chromatid is one of two identical halves of a replicated chromosome. 1Two of the subunits are SMC1 and SMC3 both of which have a 50 nm long coiled coil structure connecting a head domain and a hinge domain. Once all the chromosomes have properly attached to microtubules an enzyme known as separase becomes active and cleaves cohesin thereby triggering the separation of sister chromatids to opposite poles Figure 1.
Following DNA replication the chromosome consists of two identical structures called sister chromatids which are joined at the centromere. Diplotene marks the dissolution of the synaptonemal complex and separation of the homologous chromosomes of the bivalents except at the sites of cross-over. Solution for Non-sister chromatids Sister chromatids Sister chromatids 2 3.
Recall during prophase I homologous chromosomes line up in pairs gene-for-gene down their entire length forming a configuration with four chromatids known as a tetrad. Pairs of homologous chromatids are divided in half and distributed randomly into new diploid. Pairs of homologous chromosomes are divided in half and distributed randomly into new haploid cells.
Start your trial now. Most of the genes carried on the X chromosome do not have counterparts on the tiny Y chromosomes and the Y has genes lacking on the X. A pair of sister chromatids is called a dyad.
A sister chromatid refers to the identical copies formed by the DNA replication of a chromosome with both copies joined together by a common centromere. At this stage non-sister chromatids traverse at areas called chiasmata. First week only 499.
Our results indicated that the separation of sister chromatids was the most significantly dysregulated pathway during the transition from cirrhosis to HCC with the up-regulation of 12 hub genes. During cell division the chromosomes first replicate so that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes. It is one of the final phases of genetic recombination which occurs in the pachytene stage of prophase I of meiosis during a process called synapsis.
Here the paired chromosomes start to separate from each other into two pairs of chromatids. One of the most miraculous events in the human cell cycle is the concurrent separation of 46 pairs of sister chromatids. Basically the crossing over of genetic material between the non-sister chromatids occurs in this phase.
If crossing over did not occur until sometime during meiosis II sister chromatids which are identical would be exchanging alleles. At this point the chromatids are very close to each other. The steps follow one another without interruption.
The combined and duplicated chromosomes are called bivalents or quadruplicates which have two chromosomes and four chromatids with one chromosome originating from each parent. Chromatids break and there is an exchange of homologous parts between nonbetween non--sister chromatids.

Sister Chromatids And Non Sister Chromatids What Is The Difference Now I Know

What Is The Difference Between Sister Chromatids And Homologous Chromosomes Lisbdnet Com
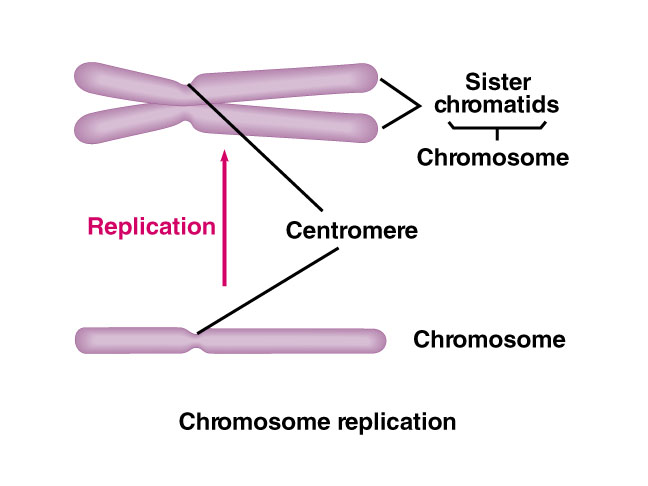
Sister Chromatids The School Of Biomedical Sciences Wiki
Difference Between Sister And Nonsister Chromatids Definition Features Role In Cell Division
Difference Between Homologous Chromosomes And Sister Chromatids Difference Between
Difference Between Sister And Nonsister Chromatids Definition Features Role In Cell Division

Meiosis I Biology For Majors I
After The S Phase In The Cell Cycle Do The Sister Chromatids Consider Homologous Quora
What Is The Difference Between Sister Chromatids And Non Sister Chromatids Quora
Difference Between Sister And Nonsister Chromatids Definition Features Role In Cell Division

Sister And Non Sister Chromatid Chromatid Homologous Chromosome Paternal Maternal Chromosome Youtube

Meiosis I Biology For Non Majors I

Difference Between Homologous Chromosomes A Pair Of Homologous Chromosomes And Sister Chromatids Stock Illustration Download Image Now Istock

Model For Transitions Of Sister Chromatids Between Different Kt Mt Download Scientific Diagram

Meiosis Ii Biology For Majors I
What Are Sister Chromatids Science Abc

Difference Between Sister And Nonsister Chromatids Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms


Comments
Post a Comment